Microservice Deployment Pipeline on Kubernetes
“Microservices Deployment Pipelines” is a daunting topic for anyone. I am going to explain how I built a Microservices Deployment Pipeline on Kubernetes. This project is inspired by Croc Hunter repo.
These are the things you must know in order to continue.
- Docker( Dockerfiles etc.)
- Jenkins( Jenkinsfiles, Pod Templates etc.)
- Kubernetes
- Helm Charts( Basic Helm Commands)
Associated Repositories
- Microservice Repo which contains the Application.
- Infrastructure Repo which can be used to deploy Jenkins and the Ingresses.
- Pipeline Lib Repo which has the Support Libraries for the Deployment.
Environments( Kubernetes Clusters)
qastagingproduction
How the pipeline works
- Commits to
devbranch goes intoqaenvironment releasebranches go intostaging- Pull Requests go into
staging - When a Pull Request is merged with
masterit gets deployed inproduction
Stages of a Deployment
You will be developing the application on develop branch. When you are ready to go into production a release branch is created. When you create a Pull Request from a release branch, it gets built in staging and the build result is submitted to GitHub. When the Pull Request is merged the app will be deployed in productio.
Branch Restrictions can be enabled to prevent unauthorized users from pushing code to protected branches. Similarly Permissions for Branching, Creating Pull Requests, Merging Pull Request and be set based on an individual’s Role in your Organization.
1. Prebuild
In this stage we check whether the image is already available using gcloud command( This is to make sure we are not building the same image twice).
gcloud container images list-tags ${DOCKER_REPOSITORY}${DOCKER_IMAGE_NAME} --limit 9999 | grep ${GIT_COMMIT_HASH} | wc -l
In addition to that we find the current Helm Revision for Rollbacks.
2. Build
The application is built here.
This stage is only executed in qa and staging.
3. Dockerize
We are Dockerizing the app here. Git hash is used to tag the image.
This stage is only executed in qa and staging.
4. Publish
Pushes the Docker Image to Google Container Registry( You can use any Docker Registry for this)
This stage is only executed in qa and staging.
5. Dry Run
Extecuted in all three environments.
6. Deploy
Extecuted in all three environments. If the deployment is unsuccessful changes are rolled back.
Shell Scripts in the Microservice Repo
Many Shell Scripts are included in the Repo to prevent having to remember all the commands needed and to automate some of the repetitive tasks.
Shell Scripts for Docker
1-docker-create-docker-machine.shto create a Docker Machine( You will not need this if you do not have Docker Machines).2-docker_deploy-mysql.shto deploy MySQL on Docker with the schema and the data.3-docker_deploy-microservice.shto deploy the Microservice on Docker. This script uses thegradleplugin for Docker to build the Docker Image.3-docker_deploy-microservice-v2.shto deploy the Microservice on Docker. This Script does not use thegradleplugin for Docker to build the Docker Image.4-docker_cleanup.shto tear down.5-docker_remove-docker-machine.shto remove the Docker Machine( Optional)
Shell Scripts for Kubectl
6-kubectl_deploy-mysql.shto deploy MySQL on your Kubernetes Cluster. In a Production Environment, you will be using an external Database. Therefore you will not need this.7-kubectl_deploy-microservice.shto deploy your Microservice on Kubernetes.8-kubectl_cleanup.shto remove everything. You may need to remove the MySQL undeployment from this script if you are using an external Database.
Shell Scripts for Helm
9-helm_deploy.shto deploy your Microservice on your Cluster using Helm Charts. Uses Config Maps to load data into MySQL( Config Map size is restricted to 1MB)9-helm_deploy-v2.shto deploy your Microservice on your Cluster using Helm Charts. Does not use Config Maps to load data into MySQL.9-helm_deploy_mysql.shto deploy MySQL on your Cluster using Helm Charts with Data. Uses the Database scriptdb.sqlto load the data directly.
How a MySQL image is created
Official MySQL Image on Docker Hub states that your *.sql files need to be copied to /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d to be executed when the container starts for the first time.
This can be achieved in two ways.
- Build a new image with your SQL Scripts copied.
- Use the Official Image. Mount your SQL Scripts into
/docker-entrypoint-initdb.ddirectory.
I have shown both ways to deploy MySQL in my Scripts. Do remember there is a limit to Config Map size( I think it is 1MB).
Final Product
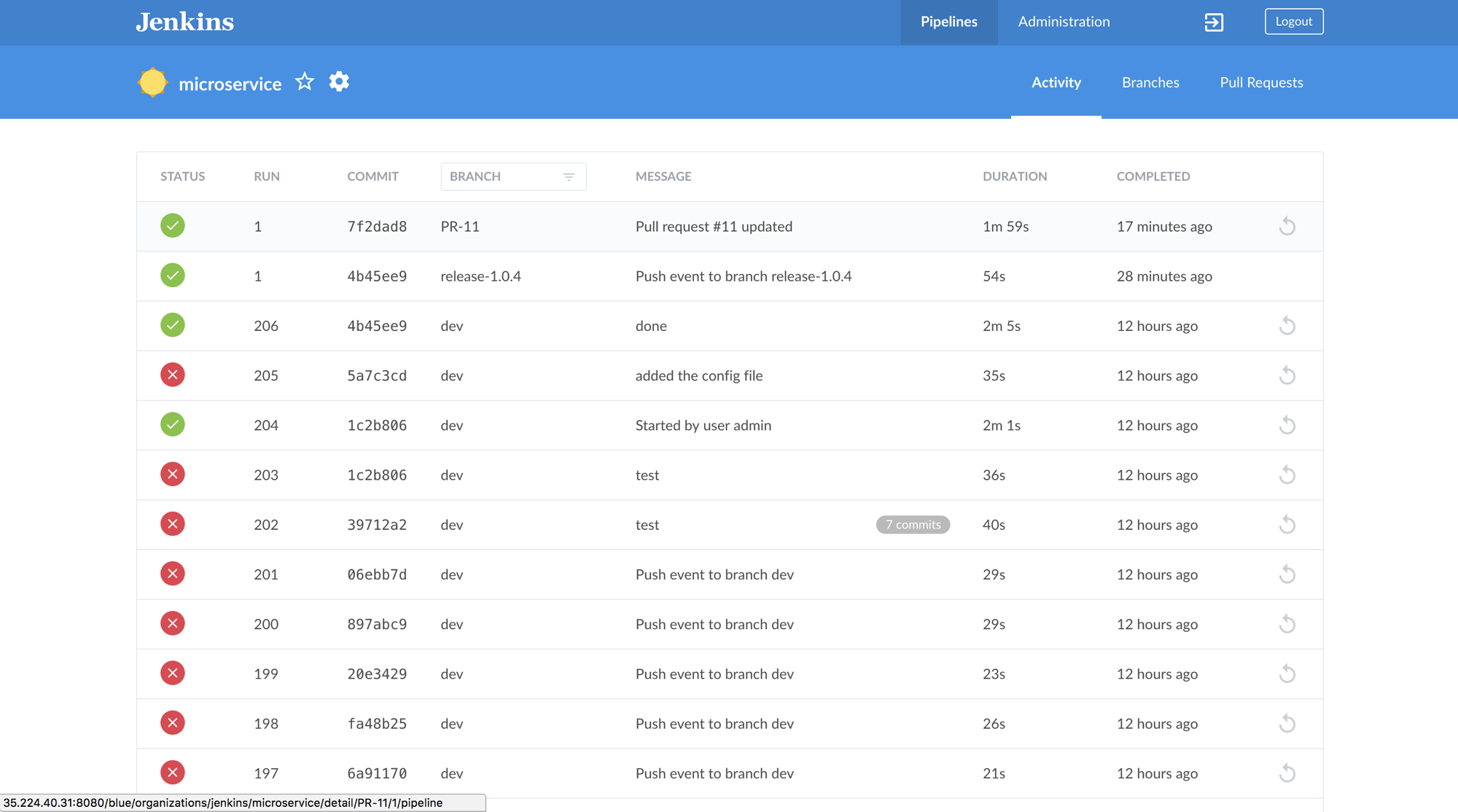
Activity Page
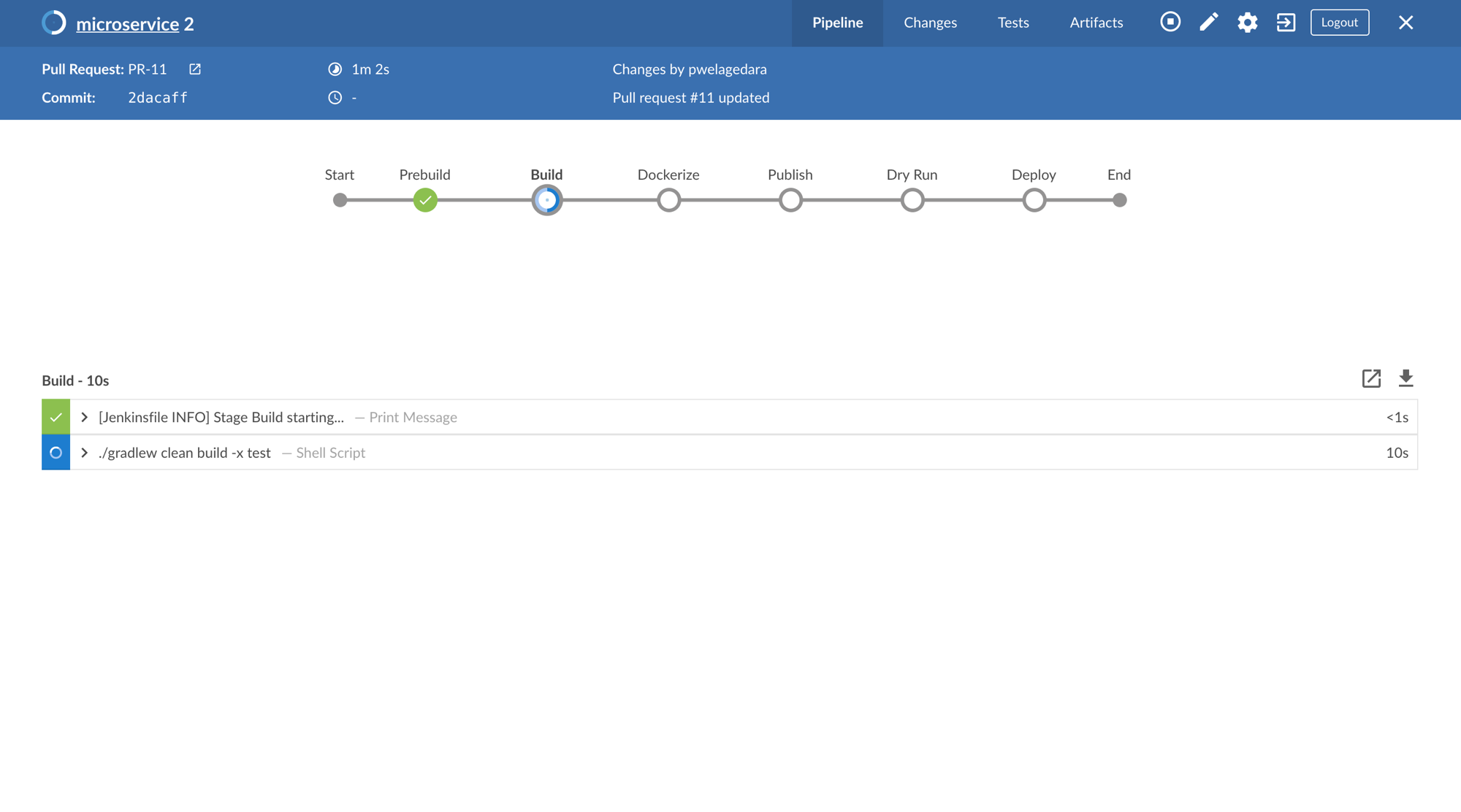
A Pull Request being Built in Staging Environment
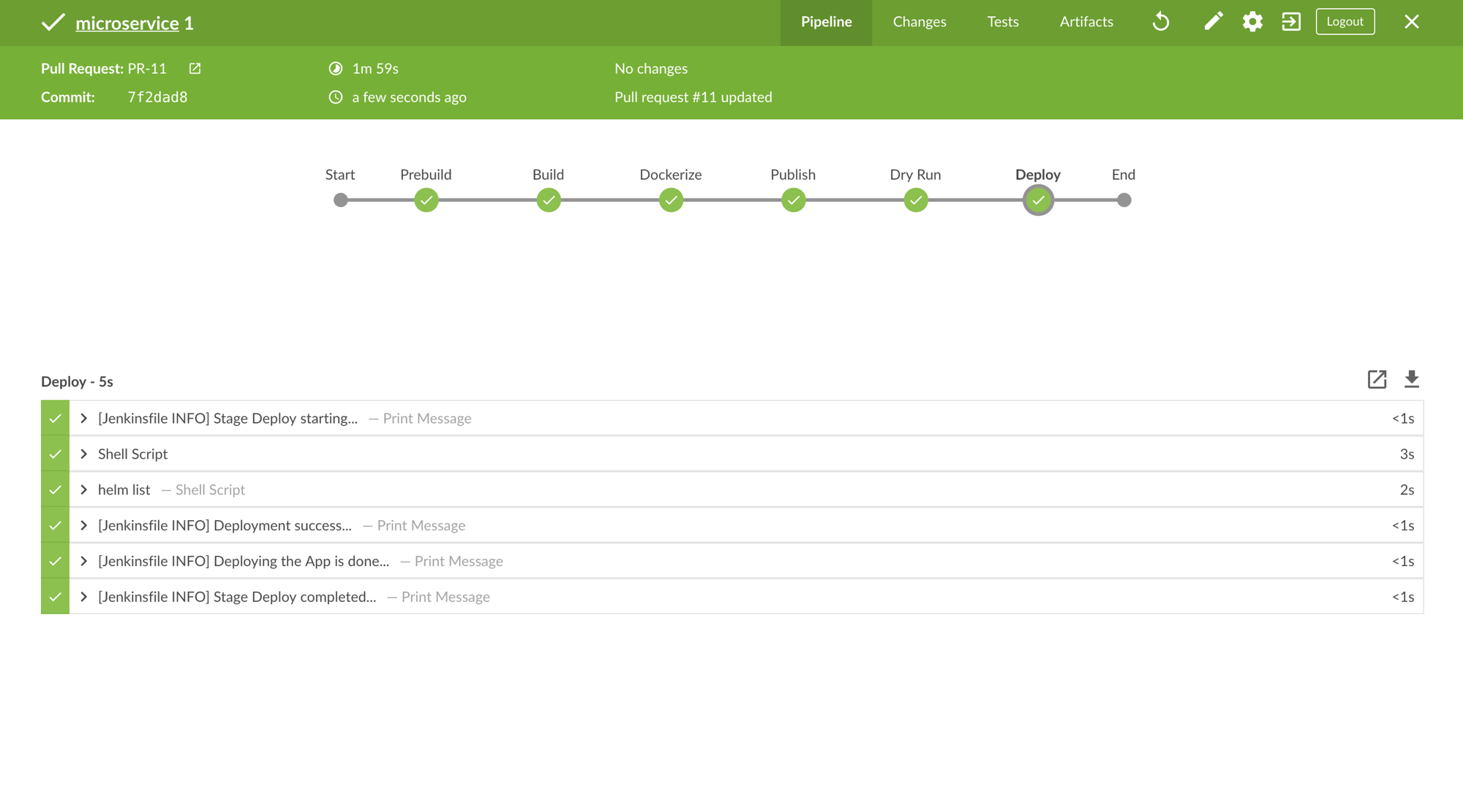
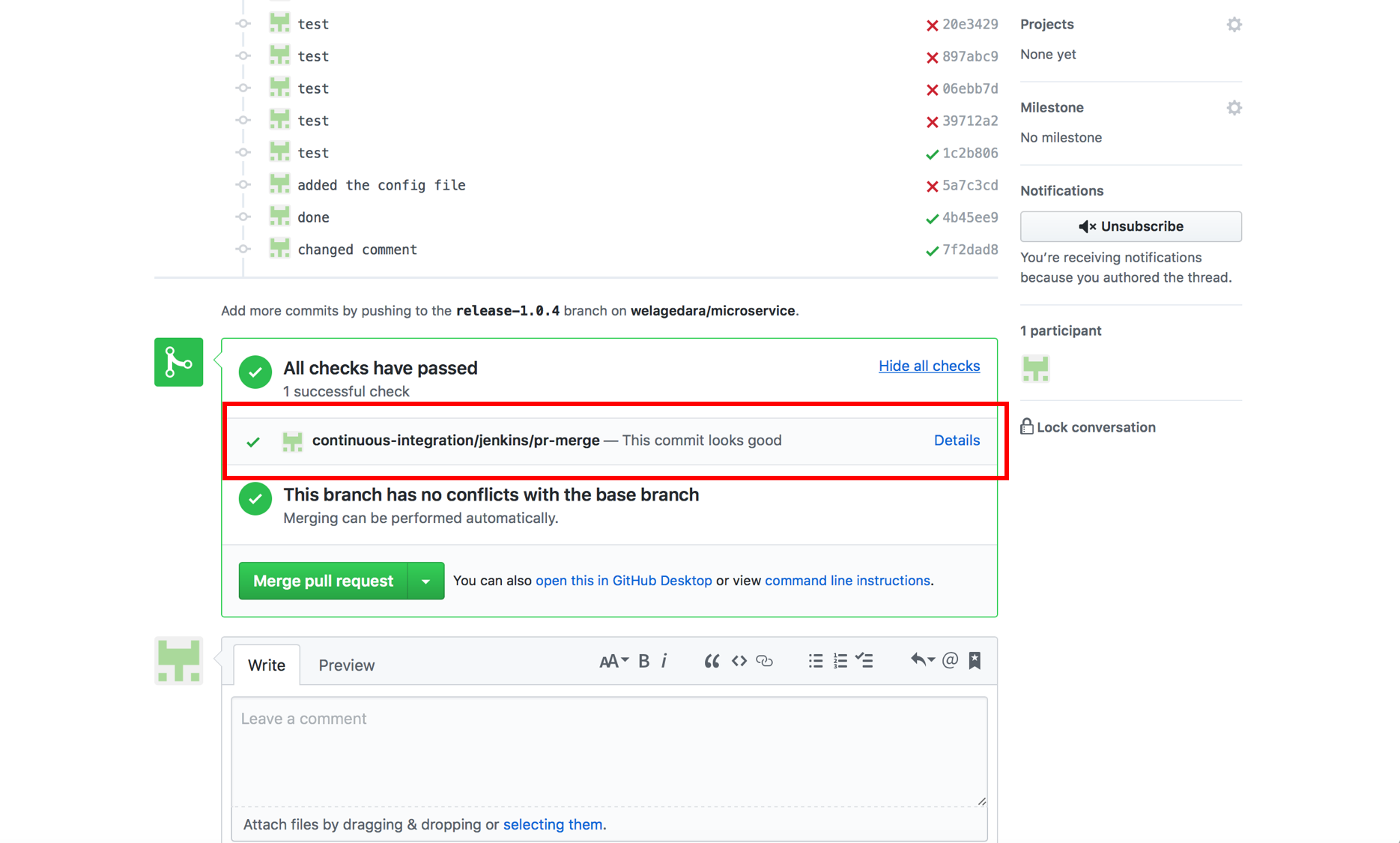
A Successful Pull Request Built in Staging Environment
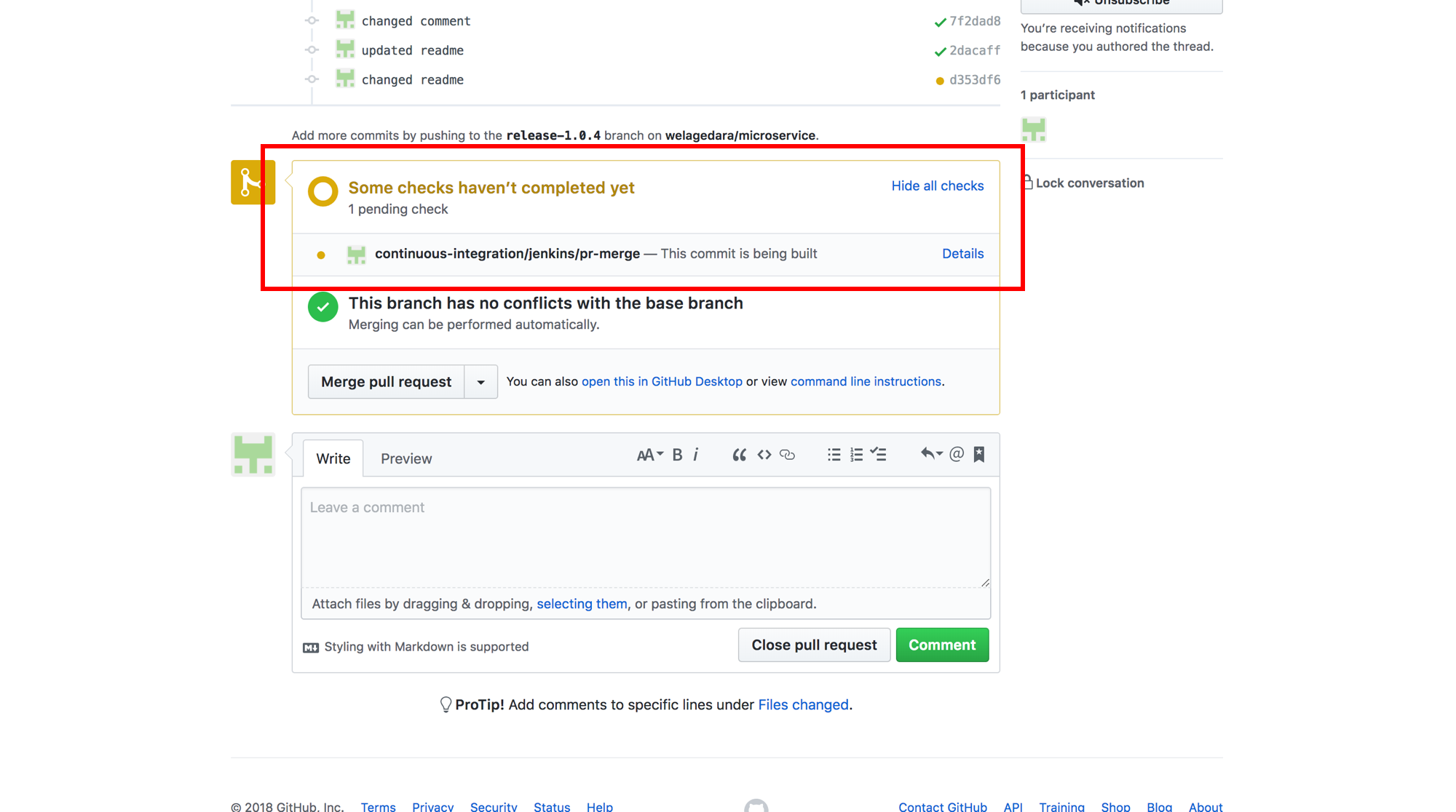
Continuous Integration System notification to GitHub when a PR is being built
Continuous Integration System notification to GitHub upon a successful PR build

Icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com